What Windows Utility Do You Use To Find The Mac Address For A System?
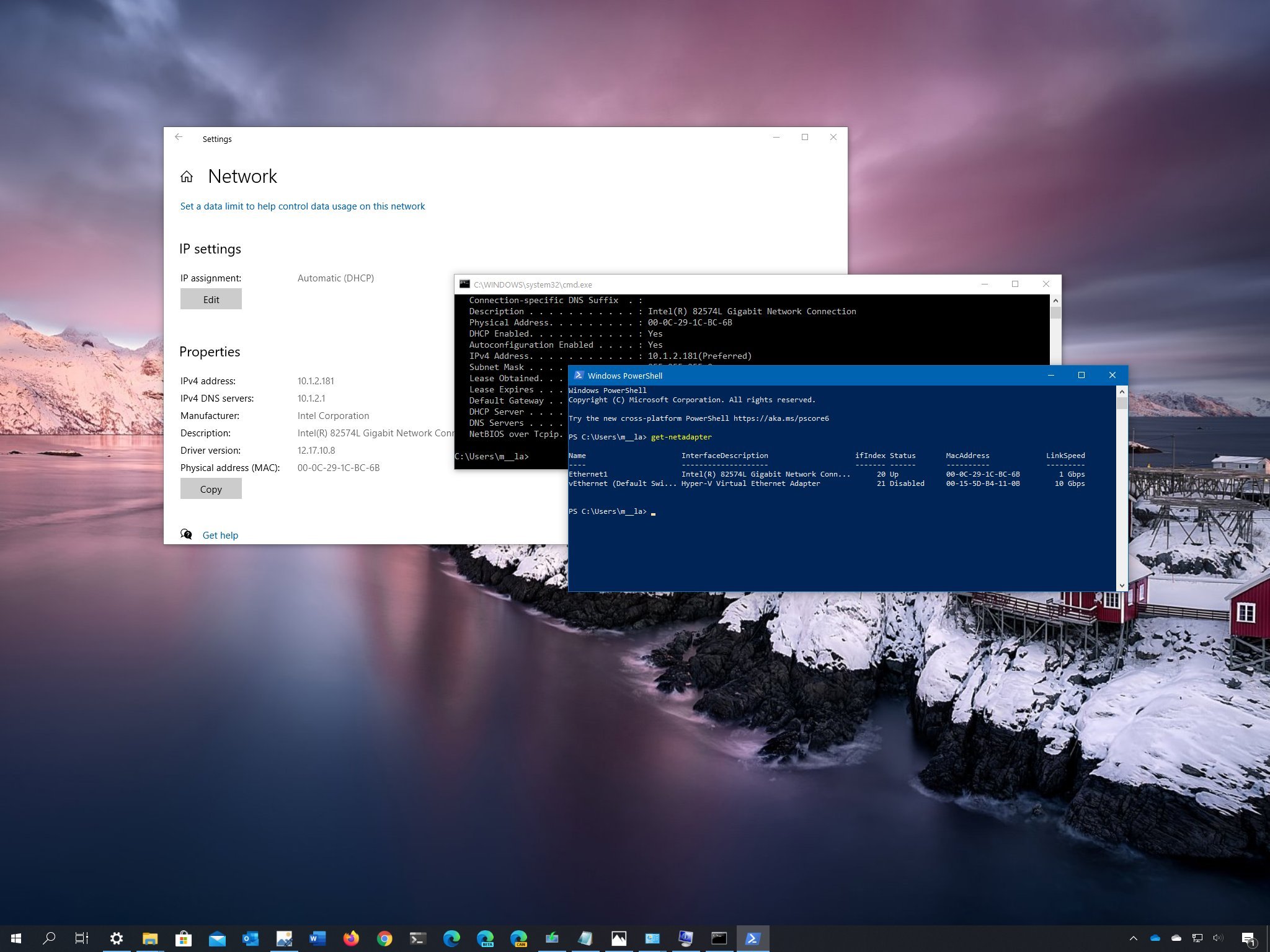
Go to ACCESSORIES. Select Command Prompt. Type: (no quotes) “ipconfig /all”. In the “ipconfig /all” results look for the adapter you want to find the MAC address of. The MAC address is the number located next to “Physical Address” in the list. We recommend using Technitium MAC Address Changer which is a freeware utility that allows the change of the MAC address. After you install the app, open it. In the Technitium MAC Address Changer window, select the network connection in the top list. Type in the new MAC address in the Change MAC Address field and press the Change now button.
- What Windows Utility Do You Use To Find The Mac Address For A System
- What Windows Utility Do You Use To Find The Mac Address For A Systematic
 -->
-->This article describes how to use the System Configuration utility to troubleshoot configuration errors.
Original product version: Windows Vista
Original KB number: 950093
Introduction
This article describes how to use the System Configuration utility (Msconfig.exe) to troubleshoot configuration errors that might prevent Windows Vista from starting correctly.
More information
The System Configuration utility finds and isolates issues. However, it is not a startup management program.
For more information about how to disable or to permanently remove the programs that run when Windows starts, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
270035 How to disable programs that run when you start Windows XP Home Edition or Windows Vista
Advanced troubleshooting
These troubleshooting steps are intended for advanced computer users. If you are not comfortable with advanced troubleshooting, you might want to ask someone for help or to contact support. For information about how to contact support, visit the following Microsoft Web site:
Microsoft Support
The System Configuration utility automates the routine troubleshooting steps that Microsoft Customer Support Services professionals use when they diagnose system configuration issues.
When you use this utility, you can select options to temporarily prevent services and programs from loading during the Windows startup process. With this process, you can reduce the risk of making typing errors when you use Registry Editor. Additionally, when you use the utility, it is easy to restore the original configuration.
When you use the System Configuration utility, you can start Windows while common services and startup programs are disabled. Then, you can enable them one at a time. If an issue does not occur when a service is disabled but does occur when the service is enabled, the service could be the cause of the issue.
You can easily reset or change the configuration settings in Windows Vista to include preferences for the following settings:
Startup options
Services that are set to start during the startup process
Programs that are set to load during the startup process
Note
These programs are specified in the Programs/Startup folders and in the registry.
Note
To use the System Configuration utility, you must be logged on as an administrator or as a member of the Administrators group.
Startup options that are available
The following startup options are available:
- Normal startup
- Diagnostic startup
- Selective startup
Normal startup
The normal startup option is the Windows default. This option enables Windows to start in normal mode together with all programs, services, and device drivers loaded.
Diagnostic startup
The diagnostic startup option enables Windows to determine which basic device drivers and software to load when you start Windows. When you use this option, the system temporarily disables Microsoft services such as the following services:
- Networking
- 'Plug and Play'
- Event Logging
- Error Reporting
- System Restore
Note
Do not use this option if you have to use a Microsoft service to test an issue.
To perform a diagnostic startup, follow these steps:
What Windows Utility Do You Use To Find The Mac Address For A System
Click Start, type
msconfigin the Start Search box, and then press ENTER.If you are prompted for an administrator password or for a confirmation, type the password, or click Continue.
On the General tab, click Diagnostic startup, and then click OK.
Click Restart.
If the issue does not occur after Windows restarts, use the selective startup option to try to find the issue by disabling and enabling individual services and startup programs.
Selective startup
The selective startup option enables you to select the programs and services that you want the computer to load when you restart the computer. You can select from the following options:
- Load system services
- Load startup items
- Use original boot configuration
By default, all these options are selected. The following rules apply to these options:
- When you click to select the check box, the option is processed when you restart the computer.
- When you click to clear the check box, the option is not processed when you restart the computer.
- When the check box is selected and when you cannot click to clear the check box because it is unavailable, some items are still loading from that option when you restart the computer.
- When the check box is not selected and when you cannot click to select the check box because it is unavailable, the option is not present on the computer.
- You cannot change the Use original boot configuration option.
Note
When you click to clear the Load system services check box, you disable Microsoft services such as the following services:
- Networking
- 'Plug and Play'
- Event Logging
- Error Reporting
- System Restore
Do not click to clear this check box if you have to use a Microsoft service to test an issue.
To perform a selective startup and to troubleshoot the issue, follow these steps:
Click Start, type
msconfigin the Start Search box, and then press ENTER.If you are prompted for an administrator password or for a confirmation, type the password, or click Continue.
On the General tab, click Selective startup, and then click to clear the Load system services and Load startup items check boxes.
Click OK, and then click Restart.
If you can reproduce the issue after the computer restarts, the issue is not related to system services or startup items. In this case, the System Configuration utility will not help troubleshoot the issue.
If you cannot reproduce the issue after the computer restarts, the issue is related to either the system services or the startup items. To determine the items to which the issue is related, follow these steps:
Click Start, type
msconfigin the Start Search box, and then press ENTER.If you are prompted for an administrator password or for a confirmation, type the password, or click Continue.
On the General tab, click Selective startup, and then click to select the Load system services check box.
Click OK, and then click Restart.
If you can reproduce the issue after the computer restarts, the issue is related to one of the system services. Otherwise, the issue is related to one of the startup items.
After you determine the items to which the issue is related, follow the steps in the 'How to determine the service or startup item that is causing the issue' section to determine the individual service or startup item that is causing the issue.
How to determine the service or startup item that is causing the issue
To determine the cause of the issue, you can prevent individual services and startup items from loading when you restart the computer. You can follow these steps.
How to determine the system service that is causing the issue
Click the Services tab, click Disable all, click to select the check box for the first service that is listed, and then restart the computer.
If the issue doesn't occur, you can eliminate the first service as the cause.
With the first service selected, click to select the check box for the second service, and then restart the computer.
Repeat this process until you reproduce the issue. If you cannot reproduce the issue, you can eliminate system services as the cause. Continue to the next procedure.

How to determine the startup item that is causing the issue
Click the General tab, and then click to select the Load startup items check box.
Click the Startup tab, click Disable all, click to select the check box for the first startup item that is listed, and then restart the computer.
If the issue does not occur, you can eliminate the first startup item as the cause.
With the first startup item selected, click to select the check box for the second startup item, and then restart the computer.
Repeat this process until you reproduce the issue.
How to enable and to disable individual services and startup items
Services and startup options
The Services and Startup tabs in the System Configuration utility have the following options:
- Check boxes enable you to enable or to disable an option. To enable or to disable an option so that it loads or does not load at startup, click to select or click to clear the check box. A selected check box indicates that the option will be started or loaded at startup.
- The keyboard arrow keys enable you to move through the different options when you do not have a mouse.
- The SPACEBAR enables you to select and to clear options when you do not have a mouse.
Note
When you click to clear a check box for an item, the Selective Startup option on the General tab is automatically selected.
How to return to normal startup
After you complete your troubleshooting and fix your configuration, return to a normal startup. You can follow these steps:
Click Start, type
msconfigin the Start Search box, and then press ENTER.If you are prompted for an administrator password or for a confirmation, type the password, or click Continue.
On the General tab, click Normal startup, and then click OK.
Click Restart.
How to start diagnostic tools and other advanced tools

You can use the Tools tab in the System Configuration utility to start diagnostic tools and other advanced tools. The Tools tab also displays the path and the switches for the tools.
To start one or more of the tools that are listed on the Tools tab, click the tool that you want to start, and then click Launch. Or, click the tool that you want to start, and then press ALT+L.
References
For more information about advanced troubleshooting for general startup problems in Windows Vista, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
927392 How to use the Bootrec.exe tool in the Windows Recovery Environment to troubleshoot and repair startup issues in Windows Vista
For more information about how to use System Restore to restore Windows Vista, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
936212 How to repair the operating system and how to restore the operating system configuration to an earlier point in time in Windows Vista
For more information about how to configure Windows Vista to start in a 'clean boot' state, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
929135 How to troubleshoot a problem by performing a clean boot in Windows Vista
If these articles can't help you resolve the issue or if you experience symptoms that differ from those ones described in this article, search the Microsoft Knowledge Base for more information. To search the Microsoft Knowledge Base, visit the following Microsoft Web site:
https://support.microsoft.com
Type the text of the error message that you receive, or type a description of the issue in the Search box, and then press ENTER.

In Windows, you can do plenty of things using command line. Converting a domain name to its IP address using the nslookup command is one of them. You can also find IP address of any website’s host machine.
Here’s is the step by step procedure:
1. Click on Start button and type cmd in the search box. Press “Enter”.
2. Windows command prompt will open. Now type nslookup ftp.yahoo.com and press enter.
3. It will show you Yahoo FTP IP address. This is IP address of the server where yahoo.com is hosted. Similarly you can find host machines for any other website.
4. If you want to look up IP address of a website then type nslookup in the command prompt and press enter.
5. Now enter the domain name of any website and press enter. It will show you the IP address of that particular site. For example I typed google.com and pressed enter. It returned Google’s IP address: 209.85.231.104.
It means if I type http://209.85.231.104 in a browser’s address bar, google.com will open.
Similarly you can convert any other domain name into its IP address. You can also check the result by typing the IP address in the browser address bar.
Now, for the more tech savvy folks among you, the nslookup command is used for testing out DNS servers. The above tutorial just outlines the basic usage of this command. There’s a lot more you could do with it. We will take it up in detail in a future post.
Remember, for websites that don’t have a dedicated IP address, you could get different results each time you use this command.
The above article may contain affiliate links which help support Guiding Tech. However, it does not affect our editorial integrity. The content remains unbiased and authentic.
Read Next
4 Useful Tools to Trace an IP Address
What Windows Utility Do You Use To Find The Mac Address For A Systematic
Tracing an
